结合 MIT-6.824-2018 的 lab1 来简单写下学习MapReduce的笔记。
MapReduce Paper
MapReduce Example
我们用最经典的words count来举例介绍MapReduce模型:
对于一个三行的input file来说,我们按行进行splitting操作。每行分给不同的线程/节点,各节点单独进行mapping任务(单词分割)。各节点在shuffing阶段会进行相互通信,完成“洗牌”工作。然后各节点单独完成reducing任务并将结果输出在各节点本地文件上。最后将这些文件进行归并得到final result。
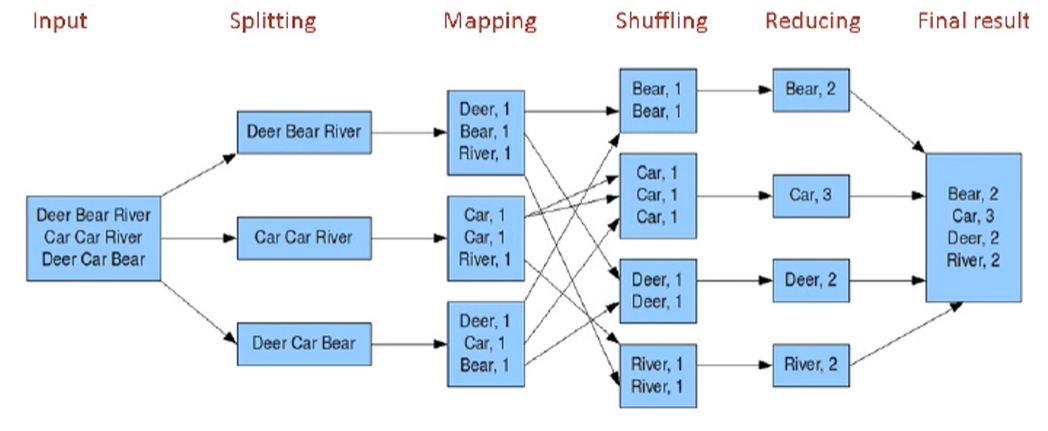
调用Map的过程发生在本地,之后的结果(键值对)作为中间文件i-j(i<=mMap, j<=nReduce)存储在当前的本地节点上。比如第一个map task会生成temp1-1, 1-2, 1-3 … 1-n共nReduce个中间文件。(虽然上图没生成)
调用shuffing的过程需要多个节点通信,选取相应的中间文件。比如对第一个reduce task,那么相应的shuffing任务会从temp1-1, 2-1, 3-1 … m-1共mMap个中间文件(位于不同m个节点)拉取键值对给相应的reduce task上。shuffing也是MapReduce代价最大的一部分。
调用reduce从shuffing那边接受结果并进行简单的合并生成reduceFile最后生成final result完成整个调用。
MapReduce Execution
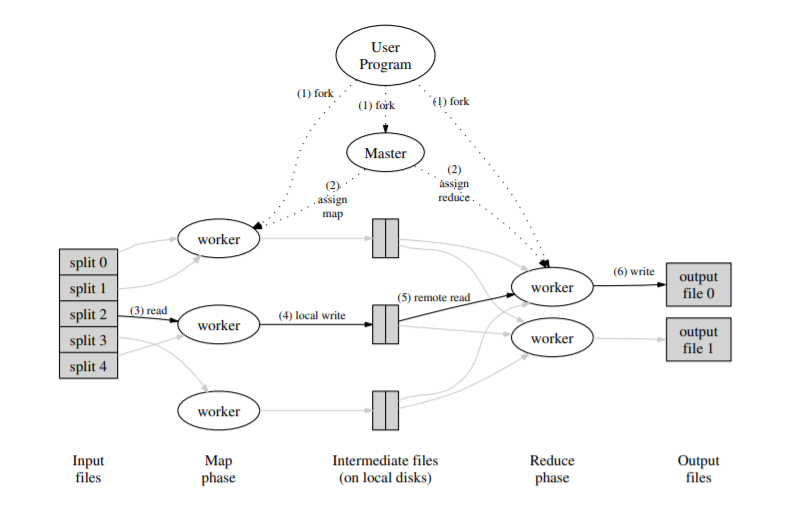
- 用户程序调用 MapReduce 库将 Input files 切成 M 个数据片度,然后用户程序在机群中 fork 大量程序副本。
- Fork 的副本中有一个特殊的程序 master,其它都是 worker 程序,由 master 分配任务。有 M 个 Map Task 和 R 个 Reduce Task 将被分配,master 将一个 Map/Reduce Task 分配给一个空闲的 worker。
- 被分配 map task 的 worker 读取相关的输入数据片段并解析出 key/value pair,然后把 key/value pair 传递给用户自定义的 Map 函数,由 Map 函数生成并输出中间 key/value pair,并缓存在内存中。
- 缓存中的 key/value pair 通过分区函数分成 R 个区域,之后周期性的写入本地磁盘。缓存的 key/value pair 在本地磁盘上的存储位置将被回传给 master,由 master 负责把这些存储位置再传送给 Reduce worker。
- 当 Reduce worker 接收到 master 发来的数据存储位置信息后,使用 RPC 从 Map worker 所在主机的磁盘上读取这些缓存数据。当 Reduce worker 读取了所有的中间数据后,对 key 排序后使具有相同 key 值的数据聚合在一起。由于许多不同的 key 值会映射到相同的 Reduce 任务上,因此必须进行排序。
- Reduce worker 遍历排序后的中间数据,对于每一个唯一的中间 key 值,Reduce worker 将这 个 key 值和它相关的中间 value 值的集合传递给用户自定义的 Reduce 函数。Reduce 函数的输出被追加到所属分区的输出文件。
- 当所有的 Map 和 Reduce 任务都完成之后,master 唤醒用户程序。此时在用户程序里对 MapReduce 的调用才返回。 在成功完成任务之后,MapReduce 的输出存放在 R 个输出文件中(对应每个 Reduce 任务产生一个输出文件,文件名由用户指定)
MapReduce Refinements
Partitioning Function
使用 MapReduce 时通常会指定 Reduce 任务和 Reduce 任务输出文件的数量(R)。我们在中间 key 上使用分区函数来对数据进行分区,再输入到后续任务执行进程。缺省的分区函数是使用 hash 方法,比如 hash(key) mod R 进行分区。
Ordering Guarantees
确保在给定的分区中,中间 key/value pair 数据的处理顺序是按照 key 值增量顺序处理的。这样的顺序保证对每个分成生成一个有序的输出文件,这对于需要对输出文件按 key 值随机存取的应用非常有意义, 对在排序输出的数据集也很有帮助。
Combiner Function
在某些情况下,Map 函数产生的中间 key 值的重复数据会占很大的比重,并且,用户自定义的 Reduce 函数满足结合律和交换律。MapReduce 允许用户指定一个可选的 combiner 函数,combiner 函数首先在本地将这些记录进行一次合并,然后将合并的结果再通过网络发送出 去。 Combiner 函数在每台执行 Map 任务的机器上都会被执行一次。一般情况下,Combiner 和 Reduce 函数是 一样的,唯一区别是 Reduce 函数的输出被保存在最终的输出文件里,而 Combiner 函数的输出被写到中间文件里,然后被发送给 Reduce 任务。 部分的合并中间结果可以显著的提高一些 MapReduce 操作的速度。
Input and Output Types
MapReduce 库支持几种不同的格式的输入数据。比如,文本模式的输入数据的每一行被视为是一个 key/value pair。key 是文件的偏移量,value 是那一行的内容。另外一种常见的格式是以 key 进行排序来存储的 key/value pair 的序列。每种输入类型的实现都必须能够把输入数据分割成数据片段,该数据片段能够由单独的 Map 任务来进行后续处理。同时也可以通过提供一个简单的 Reader 接口实现就能够支持一个新的输入类型。
MapReduce Lab
Part I: Single-worker word count
map和reduce的应用function编写,及单纯的词频统计和键值对的值合并任务。
mapF()
向mapF()传递一个文件名以及该文件的内容,mapF()将文件内容拆分为单词(毕竟对于字数统计,仅将单词用作键才有意义),并返回KeyValue类型的Go切片。
Tips: strings.FieldsFunc()可以用来拆分string,strconv.Itoa()可以将int转换成string类型。
1 | func mapF(filename string, contents string) []mapreduce.KeyValue { |
reduceF()
每个key都会调用一次reduceF()计算这个key的出现总数,并以string类型return。
Tips: strconv.Atoi()可以将string类型转换成int类型。
1 | func reduceF(key string, values []string) string { |
Part II: Map/Reduce input and output
doMap()
doMap manages one map task:读取一个输入文件inFile,并为改文件内容调用用户自定义的mapF(),最后将mapF()的输出拆分到nReduce个中间文件中。同时要保证reduce的输出为json格式以方便后续操作。
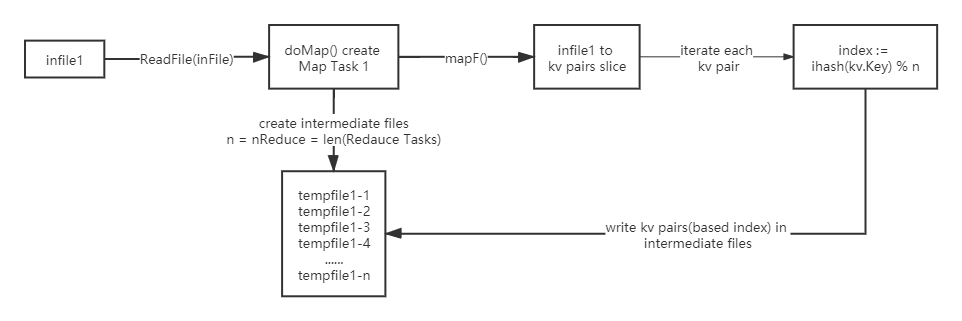
1 | func doMap( |
doReduce()
doReduce manages one reduce task:读取map tasks产生的中间文件,将其根据键值对的key排序后,为每个key调用用户自定义的reduceF()函数,最后将reduceF()的结果写到磁盘outFile文件上。因为doMap()产生的是json格式,要注意解码。
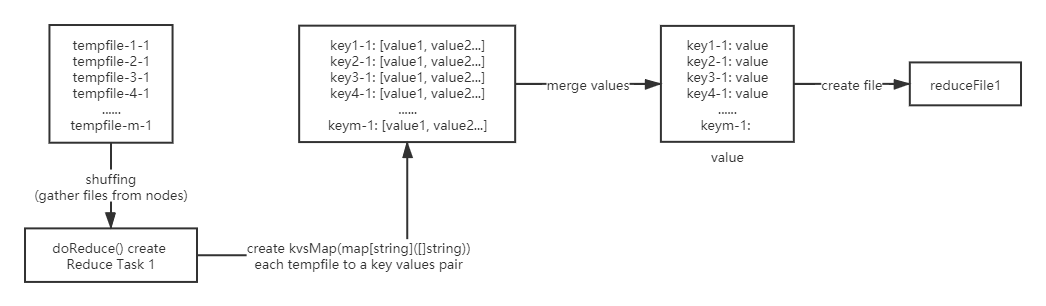
1 | func doReduce( |
Part III: Distributing MapReduce tasks
schedule()
在一次mapReduce中会调用两次schedule(),分别在map阶段和reduce阶段。schedule()将任务分发给可用的worker并等待所有任务完成后返回。registerChan参数channel为每个worker程序生成一个字符串,其中包含工作程序的RPC地址。schedule()通过call(worker, "Worker.DoTask", args, nil)(worker := <-registerChan)将Worker.DoTask RPC 发送给worker程序来通知其执行任务。
1 | func schedule(jobName string, mapFiles []string, nReduce int, phase jobPhase, |

