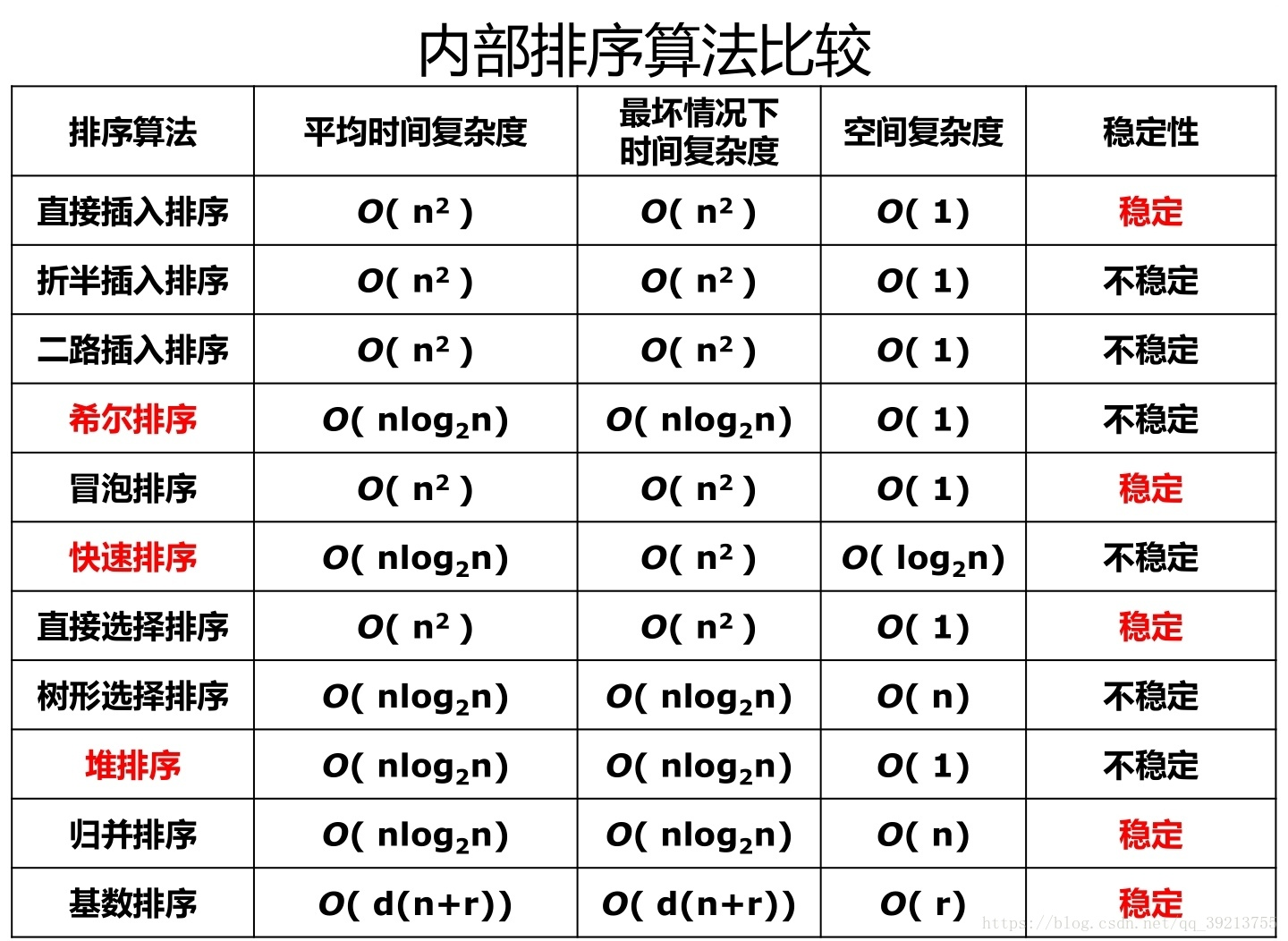
常见的nlogn排序算法介绍与C语言实现:
快速排序,希尔排序,归并排序,堆排序,排序树
快排(nlogn):
将列表以首元(a[0])为判断依据隔成两部分,第一部分全部小于首元,第二部分全部大于等于首元。(复杂度n)重复上述过程至所有元素(次数为logn)快排最优和平均时间复杂度都是nlogn,最差的情况就是数组是顺序或者逆序的,此时每一次分成两部分时,都有一部分为空(比如[1,2,3,4],比1小的部分为[],比1大的部分为剩余全部)这样会导致共需要重复n次拆分过程,时间复杂度为N^2
void quick_sort(int a[],int low,int high);
int find_pos(int a[],int low,int high);
希尔(nlogn):
将列表以不同的步长进行划分,常用n/2不断划分至步长为1。每次划分后将各子列表排序即可。希尔复杂度最优时为1.3n,分析起来好像有点复杂orz
void shell_sort(int a[],int n);
void step_wise(int a[],int D,int n);
归并(nlogn):
将列表不断二分成两份列表,当分成每个子列表的长度都为1时显然每个子列表都有序(次数logn),然后将有序的两个子列表不断合并并使之有序(复杂度n)
void merge_sort(int a[], int b[], int start, int end);
void Merge(int a[],int b[], int start, int mid, int end);
堆排(nlogn):
大顶堆(二叉树)的性质是父节点大于子节点,先通过这个性质建个堆。(tips:建堆的时候用完全二叉树的性质a[i]d的左子树为a[2*i],所以存值从a[1]开始,a[0]用来暂存值就好啦)此时a[1]一定是最大数,将a[1](堆顶)与末元a[n-1](最后一个叶节点)交换后将a[n-1]忽略,不进入下次堆排(n—)再将堆的性质恢复(logn),依次进行至堆顶(n)
void heap_sort(int a[],int n);
void sift(int a[],int r,int n);
排序树(nlogn):
右节点>父节点>左节点,建立后将该二叉树中序遍历即可。
void tree_sort(int a[],int n);
void setting(TNode* tree,int x);
void tree_order(TNode* tree);
基数排序 (d(n+r)):
依次按不同位数(d)进行关键字的比较(需要构建队列(队列大小r))
以下附实现的C语言代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node* lc;
struct node* rc;
}TNode;
void quick_sort(int a[],int low,int high);
int find_pos(int a[],int low,int high);
void shell_sort(int a[],int n);
void step_wise(int a[],int D,int n);
void choose_sort(int a[],int n);
void merge_sort(int a[], int b[], int start, int end);
void Merge(int a[],int b[], int start, int mid, int end);
void heap_sort(int a[],int n);
void sift(int a[],int r,int n);
void tree_sort(int a[],int n);
TNode* secrach(TNode* tree,int x);
void setting(TNode* tree,int x);
void tree_order(TNode* tree);
int main(){
int a[10];int b[10];
srand( (unsigned int)(time(0)) );
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
a[i]=rand()%100+1;
printf("%02d\t",a[i]);
}printf("\n");
//quick_sort(a,0,9);
//shell_sort(a,10);
//choose_sort(a,10);
//merge_sort(a,b,0,9);
//heap_sort(a,10);
//tree_sort(a,10);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) printf("%02d\t",a[i]);
}
void quick_sort(int a[],int low,int high){
if(low>=high) return;
int idx = find_pos(a,low,high);
quick_sort(a,low,idx-1);
quick_sort(a,idx+1,high);
}
int find_pos(int a[],int low,int high){
int temp = a[low];
while(low<high){
while(low<high&&a[high]>temp) high--;
a[low] = a[high];
while(low<high&&a[low]<=temp) low++;
a[high] = a[low];
}
a[low] = temp;
return low;
}
void shell_sort(int a[],int n){
int d = n/2;
while(d>=1){
step_wise(a,d,n);
d = d/2;
}
}
void step_wise(int a[],int D,int n){
for(int d=0;d<D;d++){
for(int i=d+D;i<n;i=i+D){
int temp = a[i];int j=i;
for(j=i;j-D>=0;j=j-D){
if(temp<a[j-D]) a[j] = a[j-D];
else break;
}
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
void choose_sort(int a[],int n){
//选择排序
for (int i = 0;i<n;i++){
for (int j = i;j<n;j++){
if (a[j]<a[i]){
int ex = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = ex;
}
}
}
}
void Merge(int a[],int b[], int start, int mid, int end){
//合并a、b数组并排序
int i = start, j=mid+1, k = start;
while(i!=mid+1 && j!=end+1){
if(a[i] > a[j]) b[k++] = a[j++];
else b[k++] = a[i++];
}
while(i != mid+1) b[k++] = a[i++];
while(j != end+1) b[k++] = a[j++];
for(i=start; i<=end; i++) a[i] = b[i];
}
void merge_sort(int a[], int b[], int start, int end){
if(start < end){
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
merge_sort(a, b, start, mid);
merge_sort(a, b, mid+1, end);
Merge(a, b, start, mid, end);
}
}
void sift(int p[],int r,int n){//树根p[r](可能是子树的树根)最值性质被破坏的堆
int k = 2*r;
int temp = p[r];
while(k<=n){//尽力将p[r]沉到最底,以确保整体性质的正确
if(k+1<n && p[k+1]>p[k]) k++;//防止k+1越界
if(k==n || temp>=p[k]) break;
p[r] = p[k];r = k;//先不急交换完p[r],我们看看p[r]最后能沉到哪
k = 2*r;
}
p[r] = temp;
}
void heap_sort(int a[],int n){
n = n+1;int p[n];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) p[i]=a[i-1];
for(int i=n/2;i>=1;i--) sift(p,i,n);
for(int i=n-1;i>=2;i--){
p[0] = p[1];
p[1] = p[i];
p[i] = p[0];
sift(p,1,i-1);
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) a[i-1]=p[i];
}
void tree_sort(int a[],int n){
TNode* tree = (TNode*)malloc(sizeof(TNode));
tree->lc=NULL;tree->rc=NULL;tree->data=a[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) setting(tree,a[i]);
tree_order(tree);
}
TNode* secrach(TNode* tree,int x){
TNode* p;
while(tree!=NULL){
if(x<tree->data){
p=tree;tree=tree->lc;
}
else{
p=tree;tree=tree->rc;
}
}
return p;
}
void setting(TNode* tree,int x){
TNode* p = secrach(tree,x);
TNode* q = (TNode*)malloc(sizeof(TNode));
q->data=x;q->lc=NULL;q->rc=NULL;
if(p==NULL){
p=q;return;
}
if(x<p->data) p->lc=q;
else p->rc=q;
return;
}
void tree_order(TNode* tree){
if(tree==NULL) return;
tree_order(tree->lc);
printf("%02d\t",tree->data);
tree_order(tree->rc);
}

